Човек, страдащ от диабет, е условно здрав човек
Изказване на известния диабетолог Елиът Джослин: Diabetes mellitus е болест на съвременността. С адекватно, дългосрочно лечение, мотивация и обучение, такива хора могат да живеят напълно нормален живот. По този начин могат да се избегнат хронични усложнения. Последните технически и технологични подобрения в терапията на диабета също допринасят за такова успешно протичане на това заболяване.
Diabetes mellitus е хронично прогресиращо заболяване. Това заболяване се характеризира с хронично повишено ниво на глюкоза в кръвта, което е резултат от недостатъчна секреция на инсулин или намалено действие на инсулина и може да бъде резултат от свързани нарушения.
При хора, които нямат диабет, нормалните стойности на кръвната захар са от 3,3 mmol/L до 6,1 mmol/L. След хранене стойността на глюкозата (захарта) може да се повиши до 7,8 mmol/L, но след 2 часа достига нормални стойности.
Защо казваме, че е хронично заболяване?
То е хронично, защото продължава дълго време, т.е. най-често е заболяване за цял живот. Не може да се излекува напълно, но може да се държи под контрол с адекватна терапия и промяна в начина на живот. Хроничната хипергликемия (повишена концентрация на глюкоза в кръвта) е свързана с увреждане и дисфункция на много органи, като очи, бъбреци, сърце, кръвоносни съдове и нерви. Поради това захарният диабет е основната причина за терминална бъбречна недостатъчност, слепота, ампутация на долни крайници, инсулт, инфаркт на миокарда.
Що се отнася до разпространението на това заболяване сред населението, се смята, че до 2045 г. броят на хората, страдащи от диабет, ще възлезе на около 7 милиона души и следователно, поради нарастващия брой на пациентите, diabetes mellitus захарният диабет приема формата на на пандемия.
Класификация на диабета и как се диагностицира
Класификацията на diabetes mellitus се основава на патологичните процеси, които водят до хипергликемия, така че имаме два вида:
1) Diabetes mellitus type I – среща се при деца и юноши, може да се появи и при възрастни до 30 години.
2) Diabetes mellitus type II – среща се при възрастни и все по-често при млади хора, над 30 години.
Diabetes mellitus type I възниква поради пълна или частична липса на инсулин, докато захарен diabetes mellitus type II възниква в резултат на няколко нарушения, като: степента на инсулинова резистентност, повишено производство на глюкоза, както и нарушение в секрецията на панкреатични хормони (инсулин). В допълнение към тези два вида диабет има много други специфични видове, които могат да бъдат причинени от генетични фактори, лекарства, заболявания на панкреаса, както и различни инфекции.
Критериите за диагностициране на диабет са:
– HbA1c ≥ 6.5%.
– Глюкоза на гладно ≥ 7,00 mmol/L.
– 2 часа след орално натоварване с глюкоза (OGTT) ≥ 11,1 mmol/L.
– Измерена глюкоза във всяка кръвна проба ≥ 11,1 mmol/L.
Какво е гестационен диабет и как се диагностицира?
Когато повишено ниво на глюкоза в кръвта се появи за първи път по време на бременност, тази форма на диабет се нарича гестационен диабет. Съгласно най-новите критерии диагнозата гестационен диабет (захарен диабет по време на бременност) се поставя при установяване на стойност от 5,1 – 7,00 mmol/L само при едно измерване на кръвната захар при първата контрола по време на бременност. Ако първоначалният тест е нормален, между 24-та и 28-ма седмица от бременността се прави орален стрес тест (OGTT).
Основните критерии за диагностициране на диабет при бременност са:
– Венозна плазмена глюкоза на гладно по-голяма или равна на 5,1 mmol/L.
– OGTT: глюкоза след един час по-голяма или равна на 10,00 mmol/L.
– OGTT: глюкоза след два часа по-голяма или равна на 8,5 mmol/L.
– При гестационния диабет повишеното ниво на кръвната захар се появява за първи път по време на бременност, а нивото на захарта се нормализира след раждането. Ако високото ниво на глюкоза в кръвта продължава дори след раждането, тогава това е новооткрит диабет по време на бременност.

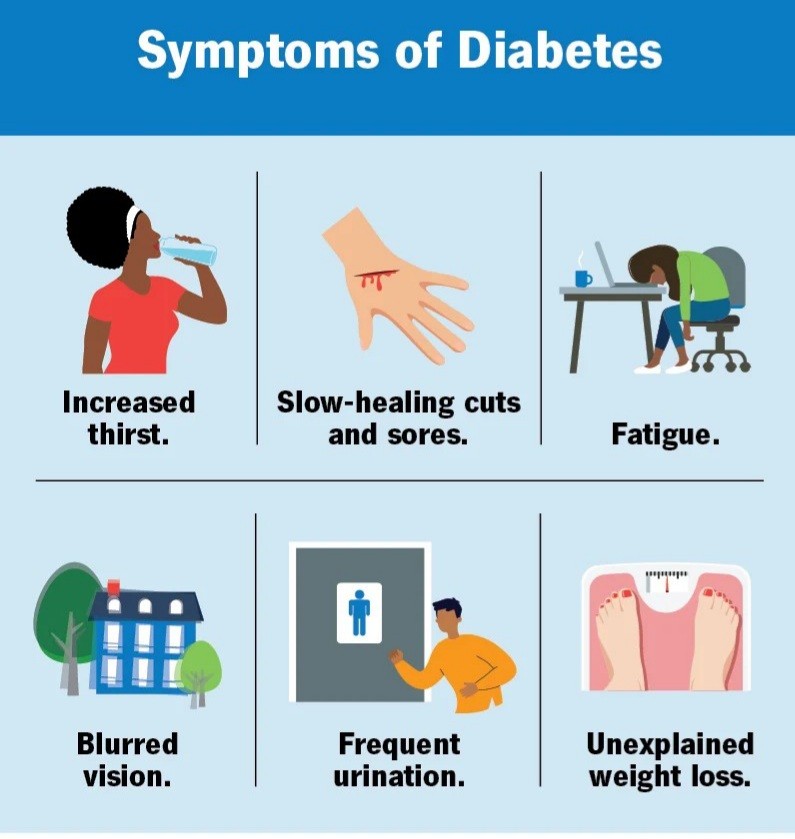
Какви са симптомите на diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus type I е форма, която възниква внезапно и може да включва следните симптоми: често уриниране, прекомерна жажда, сухота в устата, силна умора (липса на енергия), постоянен глад, внезапна загуба на тегло, замъглено зрение, чести инфекции.
Diabetes mellitus type II, известен преди като инсулинонезависим тип диабет. Представен е много повече, включва около 90% от всички пациенти. Симптомите на тази форма са много по-леки, те са по-тежка диагноза, а понякога могат да липсват, така че заболяването се диагностицира, когато вече са се появили усложнения.
Най-честото остро усложнение на диабета е хипогликемията (ниска концентрация на глюкоза в кръвта). Хипогликемия възниква, когато пациентът прилага прекомерна доза инсулин, поради нередовно хранене, повишена физическа активност, както и поради прием на големи количества алкохол. Първите признаци на хипогликемия са: изпотяване, учестен пулс, треперене, глад, бледност, световъртеж.
Какво трябва да направите в случай на хипогликемия?
Вземете храна, обогатена с глюкоза, която е сладка напитка (за предпочитане чаша кока кола), глюкозни бонбони или храна, която е обогатена с голямо количество въглехидрати.
Чесън и диабет: Как действа ферментиралият чесън при хора с диабет?
Препаратите с марка Alvitpharm съдържат в състава си черен чесън (ферментирал чесън), който има доказано хипогликемично действие (намалява повишеното ниво на глюкоза в кръвта). Аминокиселината S-alyl-L-cysteine е органично съединение, чиято концентрация е многократно по-висока във ферментиралия чесън в сравнение с пресния чесън. Според заключението на голям брой проучвания S-алил-L-цистеинът, като основно биоактивно съединение на черния чесън, има потенциала да действа хипогликемично (намалява нивото на кръвната захар) и хиполипидемично (намалява нивото на мазнини в кръвта) с минимални странични ефекти, което не е така при конвенционалната терапия при лечението на тези състояния.
Използването на S-alyl-L-cysteine подобрява както метаболитните, така и съдовите промени, което намалява възможността от различни усложнения. Доказано е, че намалява концентрацията на глюкоза, гликозилиран хемоглобин (HbA1c), урея, креатинин и пикочна киселина. S-алил-L-цистеинът има положителен ефект върху нивото на чернодробните ензими, така че доказано намалява нивото на аспартат трансаминаза (AST), аланин трансаминаза (ALT) и алкална фосфатаза (ALP). Това, което е особено интересно е, че проучването, което изследва това, сравнява лабораторните резултати след лечение с ферментирал чесън и с лекарството, перорален антидиабетик, гликлазид, и резултатите са почти идентични, а при употребата на ферментирал чесън нивото на страничните ефекти е намалена във връзка с фармакотерапията. Това означава, че S-алил-L-цистеинът може да се счита за надежден агент в терапията на захарен диабет, но все още не е вярно, че механизмът на действие на S-алил-L-цистеин при такива състояния не е дефиниран, нито разследвано ли е. Много често това е повишено ниво на кръвната захар, съпроводено с повишено ниво на холестерола и триглицеридите в кръвта. Следователно контролът на хипергликемията (повишено ниво на кръвна захар) и хиперлипидемия (повишено ниво на мазнини в кръвта) е силно свързан с намален риск от сърдечно-съдови усложнения. Много изследвания са доказали, че ферментиралият чесън има способността да намалява нивата на кръвната захар, повишава нивото на инсулина и има благоприятен ефект върху липидния статус на организма (намалява стойността на общия холестерол и триглицеридите и повишава стойността на HDL ( добър) холестерол) и регулира апетита. Хипергликемията представлява оксидативен стрес и тъй като ферментиралият чесън има много силен антиоксидантен потенциал, се препоръчва използването на черен чесън като превантивна мярка, особено при хора, които имат положителна семейна анамнеза за диабет. Също така, поради възможността да неутрализира свободните радикали, препаратите на базата на черен чесън се препоръчват и като превантивна мярка за избягване на усложнения от диабет, като инсулт, инфаркт на миокарда, ампутация на долните крайници, бъбречна недостатъчност.
Lactobacillus bulgaricus, пробиотичен щам, може да подобри антиоксидантния капацитет на ферментирал чесън за превенция на гестационен diabetes mellitus, това е доказано от едно проучване, в което са участвали 226 жени с повишен риск от развитие на това заболяване.

Препратки:
Potential of S-Allyl Cysteine, a Major Bioactive Component of Garlic, As Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Agent
Lactobacillus bulgaricus improves antioxidant capacity of black garlic in the prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus: a randomized control trial
Effect of Garlic and Aged Black Garlic on Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Animal Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Antioxidant effect of garlic and aged black garlic in animal model of type 2 diabetes mellitus
от магистър-фармацевт Радойка Костич
